openTELEMAC
openTELEMAC: open source software for environmental hydraulic calculations

openTELEMAC
openTELEMAC: open source software for environmental hydraulic calculationsWhat is openTELEMAC?
- GAIA allows studying relief evolution by considering erosion and sedimentation phenomena. It models the interactions between suspended and bed sediments to predict surface evolution on which flows occur.
- KHIONE allows accounting for all phenomena related to freezing and water melting, frasil formation, and heat exchange between phases.
- TOMAWAC and ARTEMIS are modules with different approaches that allow studying waves respectively. ARTEMIS uses the hydrodynamic calculation result to predict wave propagation, diffraction, or reflection in coastal zones and ports (linear wave, steady-state regime). TOMAWAC models wave generation (and is directly coupled to hydrodynamics) in open and coastal seas.
- WAQTEL specializes in studying water quality. With a modular architecture decomposable into sub-modules, it allows studying in particular oxygenation (with a naive model or more complex models that can include photosynthesis), algae, temperature, micropollutants and their potential sedimentation in the bed and radioactive pollutants degradation (or bacteria). It can be customized to consider more complex chemical reactions.
openTELEMAC applications
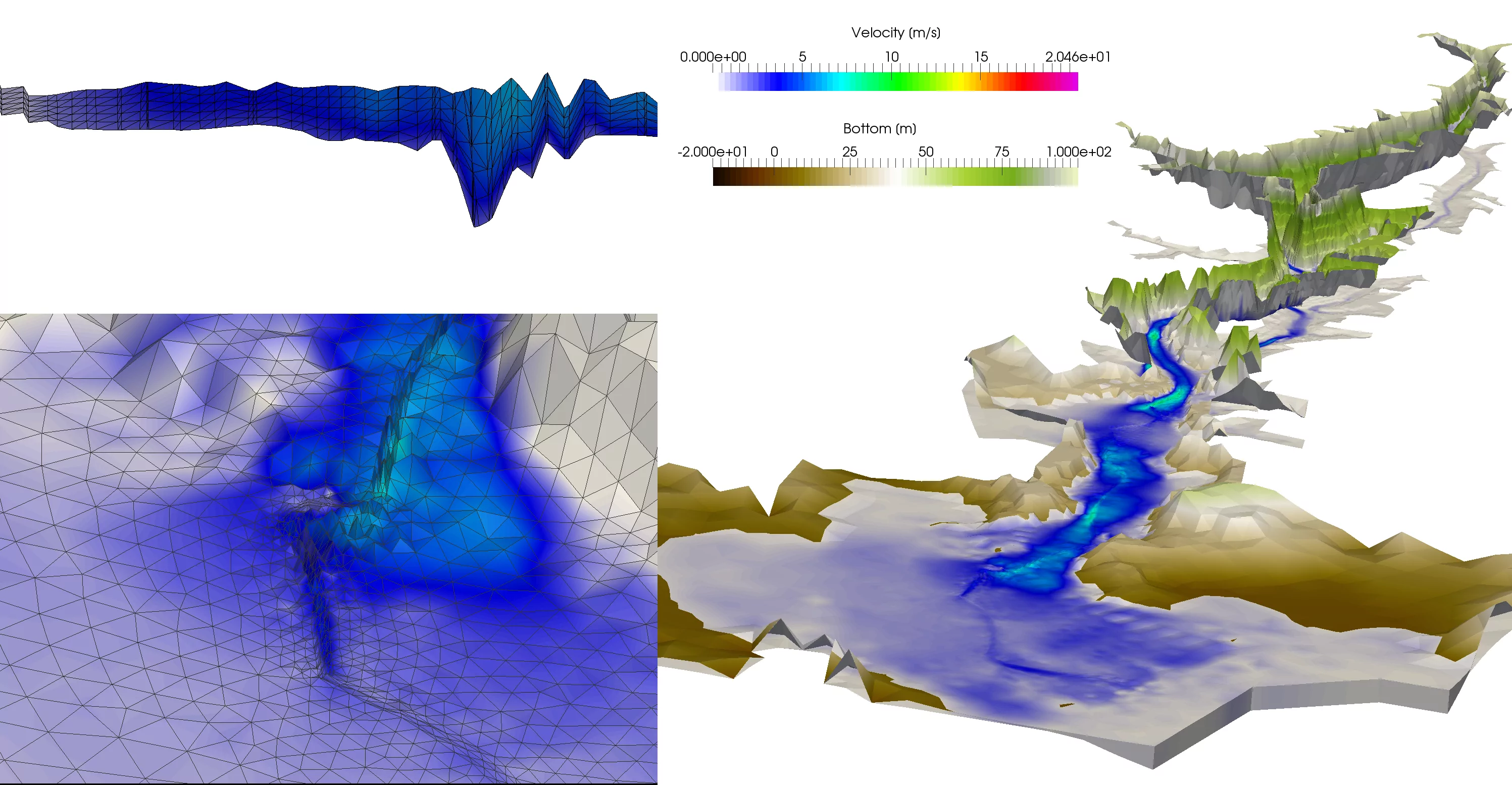
River floods, marine submersions, dam failures...
openTELEMAC is used by various organizations responsible for land planning to study flood risk zones, size the protective means or organizations to implement for water management.
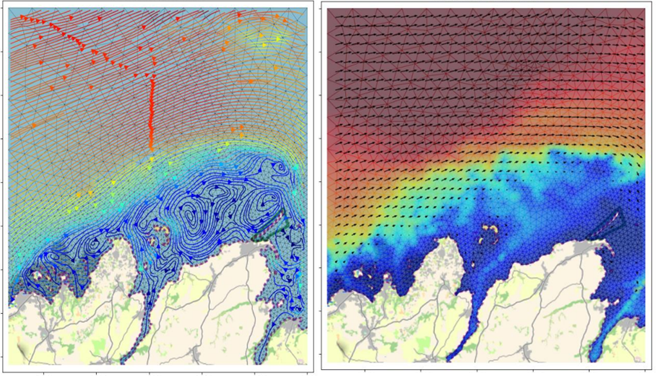
Functioning of aquatic ecosystems (fluvial, lacustrine, maritime and estuarine)
The code is widely used to model a wide variety of phenomena:
- Studies of ocean currents and waves (tidal prediction, sizing of offshore structures and coastal or port protections...)
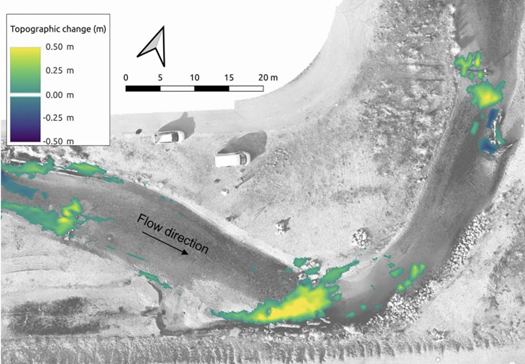
- Erosion or sedimentation of natural environments (siltation of estuaries, mangroves, water intakes etc.)
- Evolution of tracer releases, chemical or thermal in an aquatic ecosystem
- Prediction of water quality evolution (eutrophication, thermal or salt stratification...) and risk areas (heavy metals, e-coli, bacteria).
Research & education
The academic community is very active around openTELEMAC. The consortium itself includes academics and theses are regularly defended around openTELEMAC, increasingly incorporating specialized models and case studies.
openTELEMAC is also a reference in hydraulics training offered by several engineering schools and universities, in France and internationally. Its free use and the availability of its complete documentation allow students to train on a professional tool without financial barriers, while having access to theoretical foundations through user, theory, and validation documentation.
openTELEMAC events
Resources
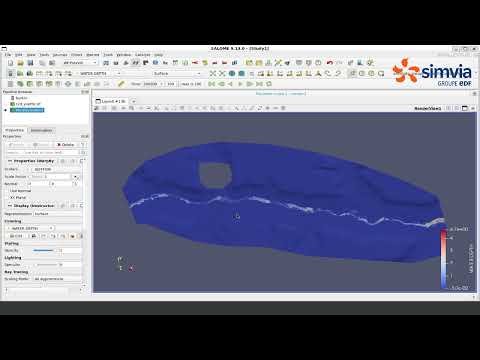
Discover how to build a complete openTELEMAC mesh workflow in QGIS using the Q4TS plugin, in this step-by-step overview.